Servo motor-controlled actuators provide precise and repeatable movements for industrial machines, utilized across many industrial applications, including those requiring high-precision positioning and cycling. So, how exactly do these actuators work, and what advantages might they bring to your project?
Let’s examine how they function to help you decide whether servo actuators fit your unique application.
How Servo Actuators Work
Servo actuators stand at the forefront of automation technology, converting electrical energy into controlled mechanical motion. Their operation hinges on a sophisticated feedback loop system, integrating sensors and advanced control algorithms.
These components work harmoniously to adjust the actuator’s output in real-time, ensuring unparalleled torque, speed, and position precision. This dynamic responsiveness is crucial in applications demanding meticulous control and repeatability, from CNC machinery to advanced robotic systems.
What is a Servo Actuator?
In industrial automation, a servo actuator is a pivotal component. Commanded by a control system, it’s a sophisticated device designed to execute controlled movements.
These actuators are renowned for their precision and efficiency, utilizing a servo motor to control the motion accurately.
Configured for linear or rotary motion, the versatility of servo actuators makes them indispensable in many automation tasks, ranging from simple conveyor systems to complex robotic arms.
Linear Servo Actuators
These actuators move machine parts linearly, typically executing back-and-forth motions. They exert a mechanical force, facilitating straightforward linear movement.
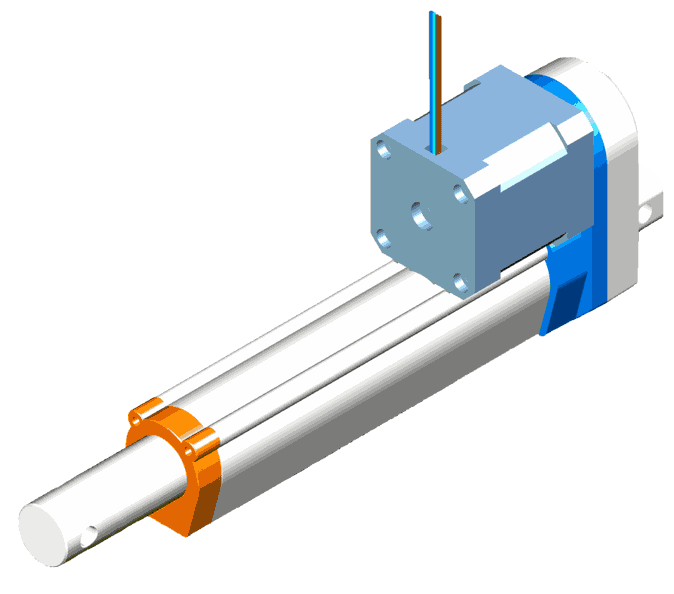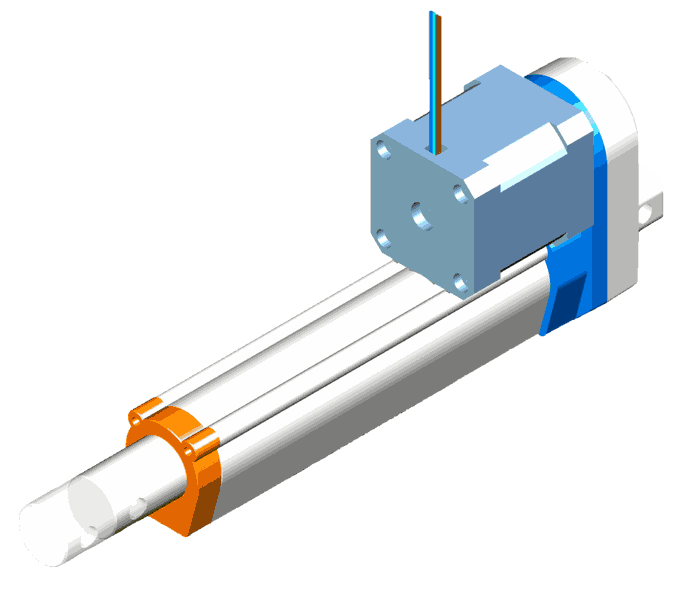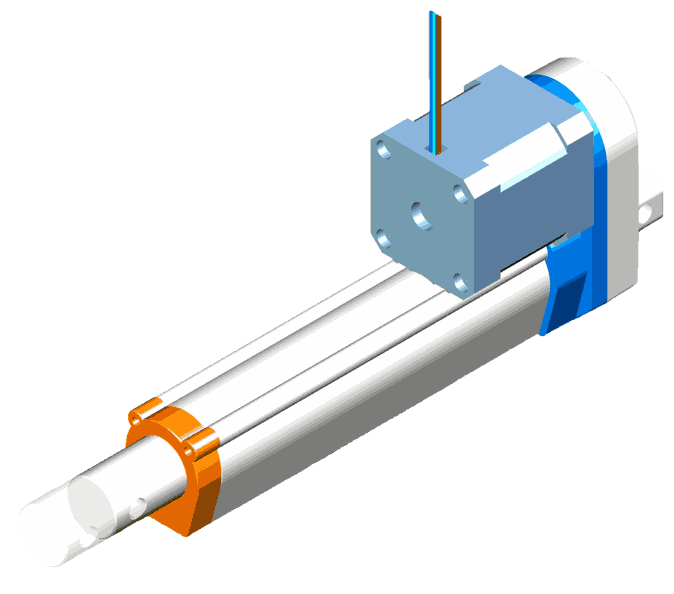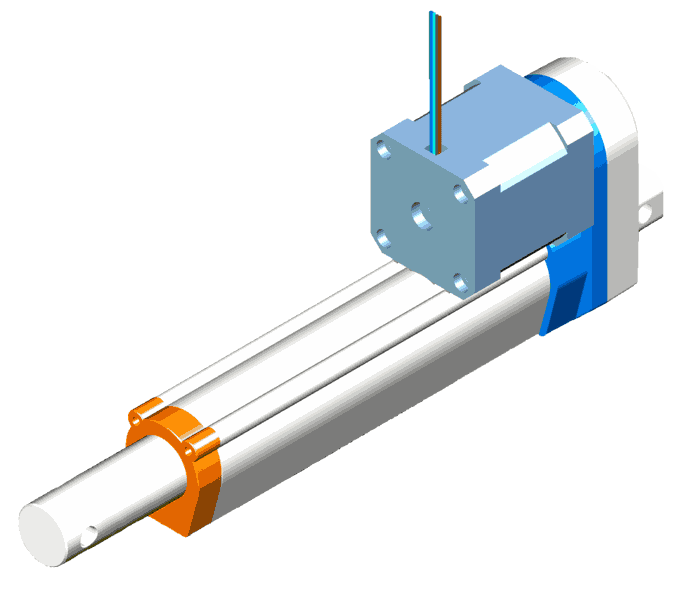
The core components include a rotary synchronous servo motor known for its high-speed rotational output. This output is then amplified in terms of torque by gearboxes.
Finally, the rotary motion is converted into linear motion through mechanisms like belts, leadscrews, or ballscrew assemblies. Each mechanism offers its balance of performance and cost considerations, enabling tailored solutions for diverse linear motion requirements.
Rotary Servo Actuators
Rotary actuators excel in creating circular motion, either in fixed degrees or continuous rotation, which is essential for various applications.
The heart of these actuators is an electric motor, typically of the induction type, which effectively converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. This conversion results in rotational torque on the output shaft, a fundamental aspect for applications like mixers, fans, saws, and pumps.
When integrated with a position sensor, these motors can accurately circularly position payloads.
What is the Purpose of Servo Actuators?
At their core, servo actuators create precise movement in machines by converting supplied energy into mechanical force. This transformation is key in tailoring the actuator’s output to the specific motion requirements of various industrial applications, whether they involve linear or rotary servo actuators.
Many favor rotary servo actuators for their adaptability because they generate a circular motion that can seamlessly convert into linear motion, typically facilitated by mechanisms like pulleys and belts.
This ability to convert rotational movement into linear displacement allows for efficient transport of objects from one point to another. Their versatility in motion control makes them an ideal choice for a wide range of industrial scenarios, where precision and adaptability are paramount.
In every application, the primary objective of servo actuators remains the same: to enable effective and controlled mechanical movement within a machine, aligning with the principles of actuation products and power density.
What are the Four Types of Actuators?
The industrial world utilizes various actuators, including:
- Hydraulic
- Pneumatic
- Electric (non-servo)
- Servo actuators
Each type has its strengths, with servo actuators particularly lauded for their precision and programmability. This capability makes them the go-to choice for applications requiring exact movement and fine-tuned control.
What is the Difference Between a Linear Actuator and a Servo Actuator?
While linear actuators are designed for straightforward, unidirectional motion, servo actuators offer more control. This includes the ability to precisely dictate movement patterns, speed, and positioning, making them more suitable for complex automation tasks.
Distinguishing between linear and servo actuators is key to selecting the suitable component for specific industrial applications.
Servo Actuators Advantages
Servo actuators are pivotal in industrial settings due to their numerous advantages, which include superior performance, precision control, compact size, and low energy consumption. These attributes make them ideal for various demanding industrial applications and environments.
- Superior Performance: A servo actuator is renowned for delivering exceptional torque, speed, and power throughout its lifespan. This consistent, dependable performance is vital in industrial contexts where reliability and efficiency are paramount.
- Precision Control: One of the hallmark features of servo actuators is their ability to enable highly accurate motion control. This precision is mandatory in applications where exact positioning and near-perfect repeatability are crucial, ensuring operations are carried out with the utmost accuracy.
- Compact Size: The design of linear and rotary servo actuators is remarkably size-efficient. This compactness is crucial in applications with space or weight constraints, such as robotics systems, where integrating servo actuators helps create more compact and lightweight solutions.
- Low Energy Consumption: Servo actuators offer high power density, which translates to reduced overall energy consumption. This cost-effectiveness efficiency aligns with the growing need for more sustainable, energy-efficient industrial solutions across various sectors.
These advantages collectively contribute to the growing adoption of servo actuators in diverse industrial applications, underlining their role as a transformative component in modern machinery.
Applications for Servo Actuators
Servo actuators are integral to the nuanced requirements of medical devices and the demanding environments of manufacturing lines. They provide the necessary precision and reliability for many applications, affirming their status as a critical component in the evolution of industrial automation and control systems.

Material Handling
Precise automation is critical in material handling, where speed, accuracy, and care are crucial to meet consumer demands. A linear or rotary servo actuator grants material handling systems a new control caliber, ensuring materials are transported quickly and safely to their proper destinations.
Functional safety tools, such as emergency brakes and Safety PLCs, can elevate these solutions to maximize safety while keeping the supply chain fluid.
Medical Devices
Medical devices require pinpoint accuracy to support patient safety, comfort, and care outcomes. This is where a rotary or linear servo actuator excels. Medical tools requiring precise motion control, such as patient lifts, can harness servo actuators to properly position objects or patients for treatment.
Purpose-built brakes and clutches can further improve these medical applications.
Robotics
Robotics is an ascendant force in automation, sweeping diverse industrial applications from metalworking and spot welding to packaging and plastics. With servo actuators, machine builders can create more dependable, efficient robotic systems that move tools, parts, or materials with unmatched precision.
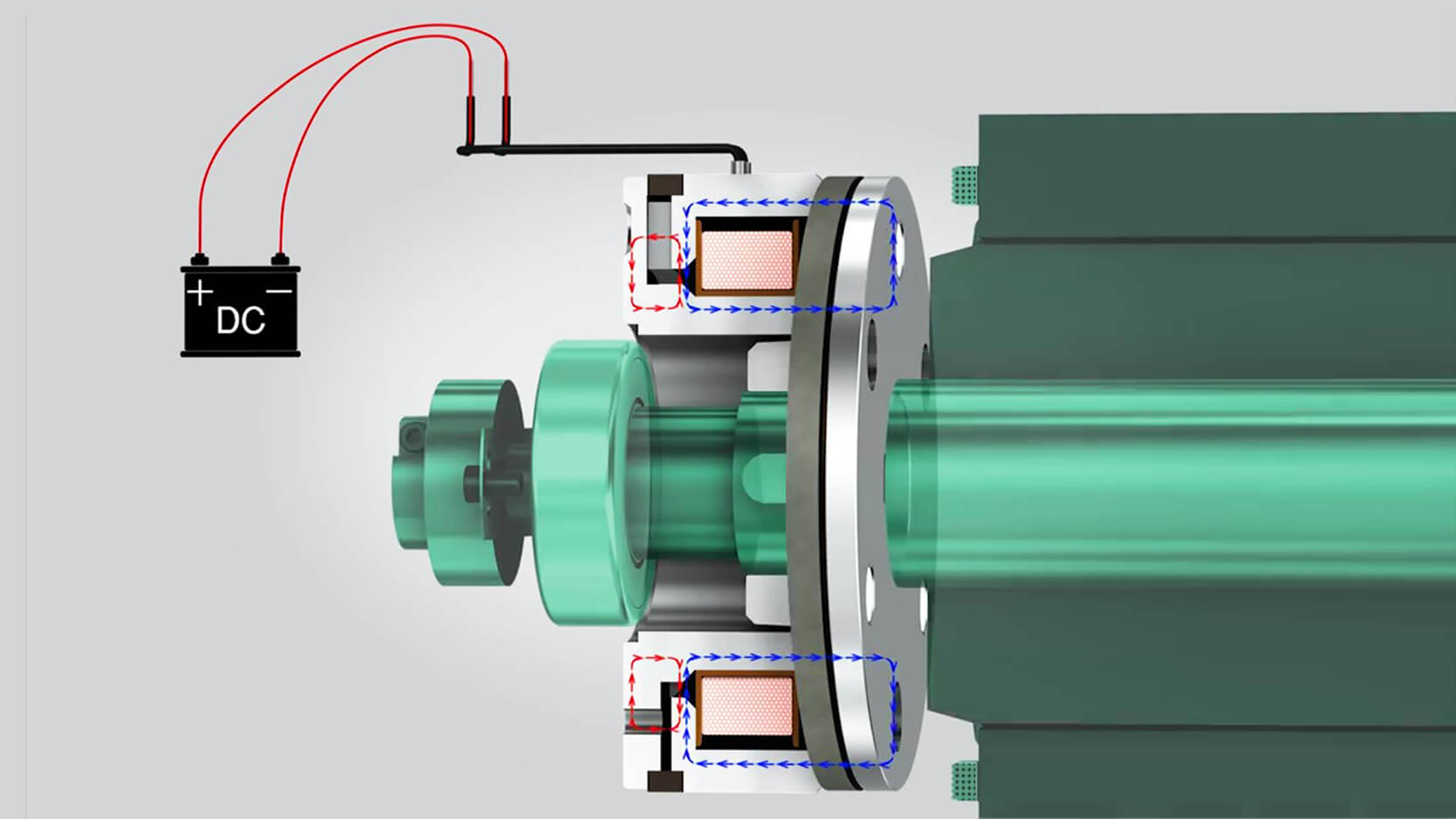
KEB: Your Partner in Automation & Control
KEB develops world-class products that work with actuators to drive performance, including servo motors and brakes for electric linear actuators.
Servo actuators are essential components in the landscape of modern industrial automation. Their ability to offer precise, efficient, and versatile solutions is vital for many applications.
Understanding their function and benefits is crucial in selecting the proper actuator for your needs.
Let's Work Together
Connect with us today to learn more about our industrial automation solutions—and how to commission them for your application.