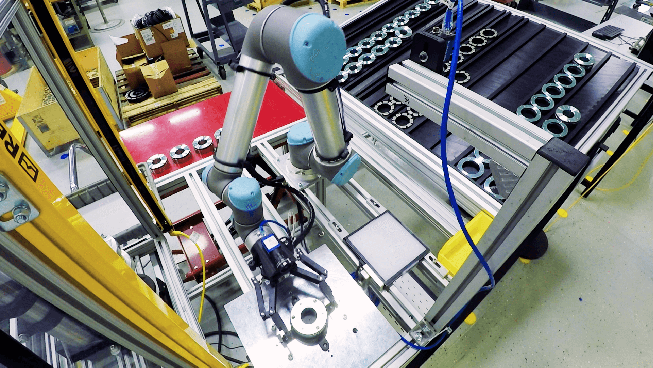
Automation and robotics have advanced rapidly in the last decade, shifting the industrial landscape and labor markets worldwide. These technologies enable robots and machines to complete various tasks typically carried out by people across many industries, from healthcare, packaging, and agriculture to material handling. Indeed, many businesses already leverage robots to automate and streamline work processes, particularly those in thriving manufacturing countries like Germany and China.
While this “robotics and automation revolution” will undoubtedly drive productivity and efficiency for many markets, it also threatens to disrupt existing sectors and workforces. Some jobs may become obsolete, while others must change significantly to account for these new tools. That said, this stunning technological movement stands to leave new job opportunities (and entirely new industries) in its wake as well.
How Many Jobs Will Be Lost to Automation by 2030?
According to a 2019 analysis report from Oxford Economics, up to 20 million manufacturing jobs worldwide may be replaced by robots by 2030. This is partly due to the nature of manufacturing environments and factory jobs, which often involve manual tasks that can be effectively automated.
Workflows involving repetitive steps and physical skills are some of the most likely to be disrupted by robotics and automation. For example, the need for assembly line workers may decrease as robotics systems become better at fabricating and assembling parts. Robots can be programmed to repeat the same motion or manual task with unmatched precision, even compared to experienced workers. Many jobs may be lost to automation in the coming years.
In addition, if you read through the 2022 report from the US Government Accountability Office to congress entitled WORKFORCE AUTOMATION: Insights into Skills and Training Programs for Impacted Workers you’ll see some of the skills that will be less valuable in the future, as well as skills that will continue to be valuable in the years to come. “…one study noted that the skills most vulnerable to automation are routine cognitive and physical skills, such as operating machinery or collecting and processing data, while the least vulnerable are skills such as creativity, social skills, management, and planning.” – (page 15 & 16)
Automation Creates Job Opportunities in Manufacturing and Beyond
While automation and robotics may displace workers in the coming decades, they also have the potential to fuel new markets and jobs. The demand for IT and digital skills will grow in the manufacturing sector as we learn how to collaborate with and maintain these systems. New types of products and manufacturing will become possible thanks to automation, fueling demand for engineers, sales reps, managers, and more across the industry.
Related: Blog – KEB America Increases Automation in Brake and Clutch Manufacturing
Related: Blog – KEB America’s ISO 9001:2015 Certified Manufacturing Practices
Related: Watch KEB America’s Cobot Automation in Brake Manufacturing
The fundamental challenge with this automation and labor shift is that it will require adaptation from workers worldwide. Manual skill sets will become less valuable in the labor market because machines can lift, trim, cut, polish, and move materials much more effectively than humans. But with this change comes an increased demand for technology, leadership, and social skill sets, in which real people remain unmatched.
The fear that a robotics revolution will create rampant unemployment across the nation is largely unfounded. It’s not a zero-sum game between people and machines. Increased use of robots by companies (especially in manufacturing) creates more economic value by helping them boost productivity and profitability. This lowers prices, improves consumer spending, and creates more jobs overall.
3 Technologies Driving Industrial Automation
Today’s manufacturers and machine builders use robotics and automation to improve efficiency, reduce manual errors, and complete repetitive tasks much faster. These systems are enabled by leading-edge control and automation technologies, including the following:
![]()
1. IoT Networks & Gateways
MQTT IoT routers connect multiple IoT devices into a single network, enabling inter-device communication and seamless data flow to and from the cloud. This industrial hardware allows businesses to gather machine data using connected sensors, which measure temperature, vibration, speed, and more. These insights help ensure that automated systems run at peak performance without workers needing to physically inspect the machine.
2. Servo Motors
Servo motors are used across many applications, from industrial production and robotics to elevator technology. These motors offer remarkable precision, force density, and power at compact sizes, making them a natural fit for robotics and automation systems. For example, servos can be used to help automate the movement of theater scenery (instead of being manually moved by stagehands). This supports repeatable, safe transitions of stages across every practice session and performance.

3. VFDs & Drives
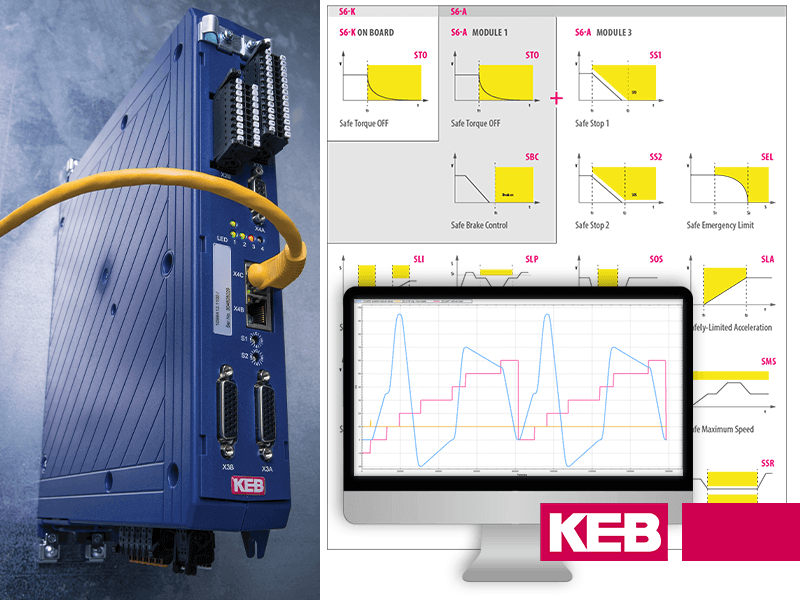
Modern VFDs and drives include useful features to coordinate and improve the safety of automated machine movements. KEB drives, for instance, can be outfitted with safety controllers to slow robots down when they move close to people or fragile assets. This “safe limited speed” function protects the robot and passersby from collisions without deactivating it entirely.
KEB: The Future of Control & Automation
As a leader in control and automation, KEB offers a variety of powerful hardware and software solutions, including motors, drives, and IoT gateways. If you’re seeking new tools to help your business improve productivity, reduce costs, and drive more efficient operations through automation, contact a KEB solutions engineer today. Our team will help you choose technologies for your unique automation challenges, applications, and goals.
Let's Work Together
Connect with us today to learn more about our industrial automation solutions—and how to commission them for your application.