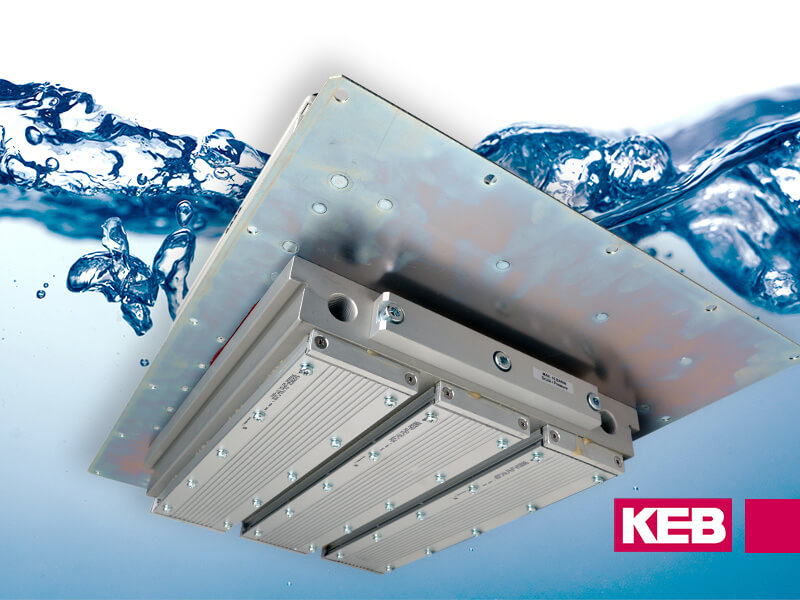
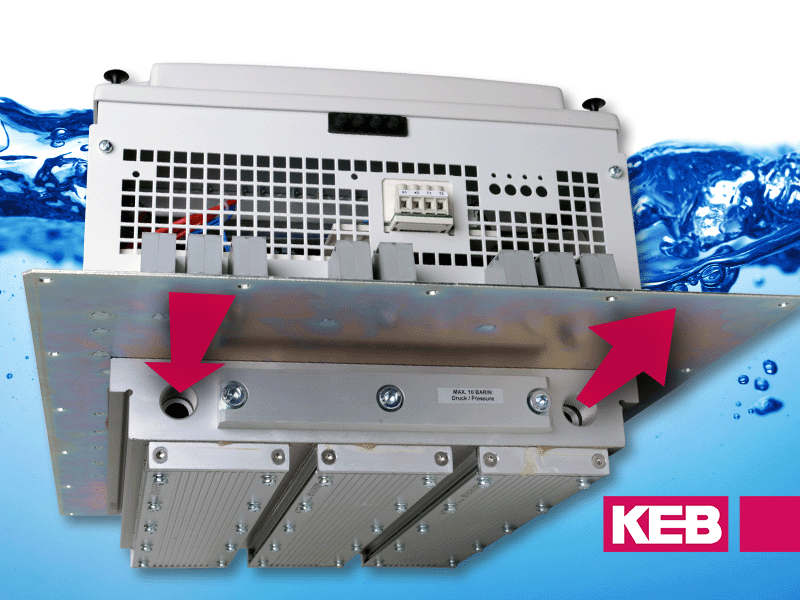
Optimize your process with Cold Plate (Flat Back) Heatsink VFDs
Selecting the right technology for your application can improve component functionality and equipment performance. The different drive technologies featured in KEB drive products are designed to provide the best solution for the application. Our standard fan-cooled heatsinks are suitable for most applications. For Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) that are used on machines with cooling pumps, the KEB Liquid Cooled VFDs are the most common option. If environmental conditions are a concern, a push-through heatsink with oversized cooling fins might be a better option since forced-air fans can become clogged with fibers (e.g. textile). Another option is the KEB cold plate or “flat back” heatsink.
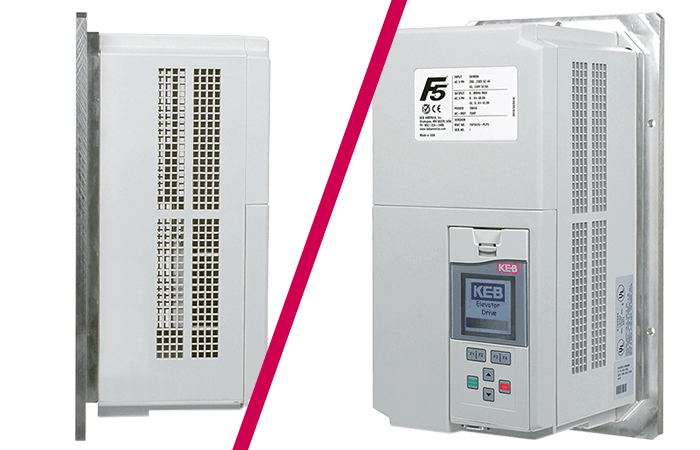
This post describes the cooling plate heatsink and when it might be the preferred technical solution for an application.
Finned Heatsink (Fan-cooled)
Most commercial VFDs use a finned heatsink made out of casted or machined aluminum. Fans push air across the large surface area of the heatsink and the heat is dissipated into the electrical cabinet. There are a few disadvantages to air-cooled drives:

- The fans and heatsink fins add depth to the drive profile – A machine designer might prefer a drive with small depth if they are limited on panel options (e.g. explosion-proof enclosure) or they need it to optimize the packaging. If a machine builder wants a drive with the shortest depth possible, then there are better options.
- Air-cooled VFDs dissipate heat into the electrical enclosure – This means that the enclosure needs to be oversized to handle the extra heat. This could lead to a larger than necessary and more costly enclosure and less than optimal packaging in the machine.
- Fans commonly fail and will likely need to be replaced at some point – Drive fans are typically one of the first VFD components to fail and this can happen within five years or less. Fans that operate continuously (24/7 duty) in hot and dusty environments will be particularly susceptible to premature failure.
- Fans add noise – This is usually a small factor, but the drive fans can be quite loud, especially for higher power applications. If noise mitigation is a goal, then this could be an important point.
Cold Plate VFDs
An alternative to air-cooled drives would be to use a drive with a flat machined heatsink surface. These are often called cold plate drives or flat back drives. The machined surface of the drive is meant to be installed on a cooling plate and the heat is transferred through conduction.
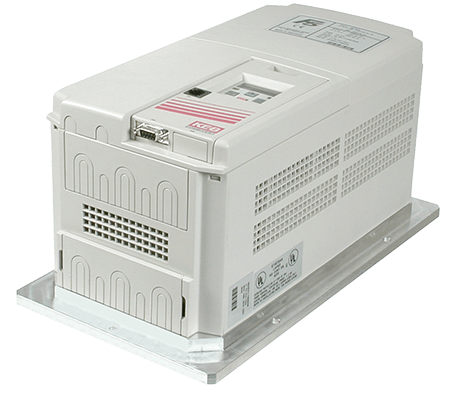
This type of cooling provides a number of technical advantages:
- The heat from the drive’s insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is more efficiently transferred via conduction rather than convection. This means that the cold plate VFD can be used in applications that might not have been possible with an air-cooled drive (e.g. high-speed applications requiring high-frequency switching).
- The VFD heat is transferred to the cooling plate and outside the drive cabinet. This results in less heat dissipation inside the panel, meaning the overall enclosure size can be reduced. This results in a smaller enclosure and better overall packaging for the machine.
The Cold Plate VFD is ideal for applications requiring small electrical enclosures
Relatively few drive manufacturers offer cold plate VFDs. Among those manufacturers, the offering is limited in size – usually to 10Hp or less. The KEB cold plate offering extends up to the R-Housing frame (F5 series) – or 125Hp in the 480V class. Finally, the cold plate option is also available for large multi-axis applications with our H6 drive.
Conclusion
KEB’s cold plate option for KEB VFDs might be interesting to machine builders looking to shrink the size of the drive panel and reduce their machine footprint. It is also a good option for environments where there might be contaminants in the air like fibers or dust that could cause fans or A/C units to prematurely fail. KEB offers the cold plate heatsink option across a number of different drive models up to 125Hp.
Any other advantages to using a cold-plate design? Can you see it working in your application?
Let's Work Together
Connect with us today to learn more about our industrial automation solutions—and how to commission them for your application.