The Importance of High-Quality VFD Power Cables
Why Do VFDs Need Quality Power Cables?
VFDs are inherently noisy devices because the output IGBTs are switching hundreds of volts on and off, thousands of times per second. Because of this reality, proper cabling and grounding techniques must be followed to mitigate the potential negative effects of this operation.

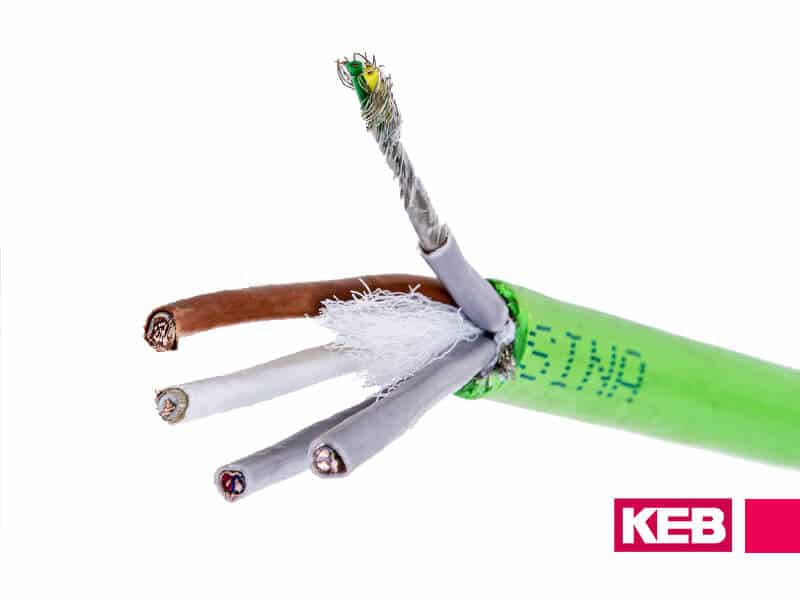
Similar to encoder feedback cables, motor power cables that connect a VFD to a three-phase motor should have these proper characteristics to efficiently conduct the current, while not interfering with other electrical components in the machine.
Grounding and Power Cable Guidelines for High Speed VFD Applications
Proper Cable Shielding
Shielding mitigates the effects of electromagnetic interference (EMI) or noise. One of the most effective and robust ways to shield the power cable is with wire mesh shielding. It is highly conductive and the mesh design helps prevent rips or breaks. EMI filters and harmonic filters are often used to further smooth out incoming and outgoing power, especially in high-power applications or when sensitive electronics are nearby.

Related Article: 7 Steps to Reducing EMI with VFDs
Benefits of High Strand Cabling
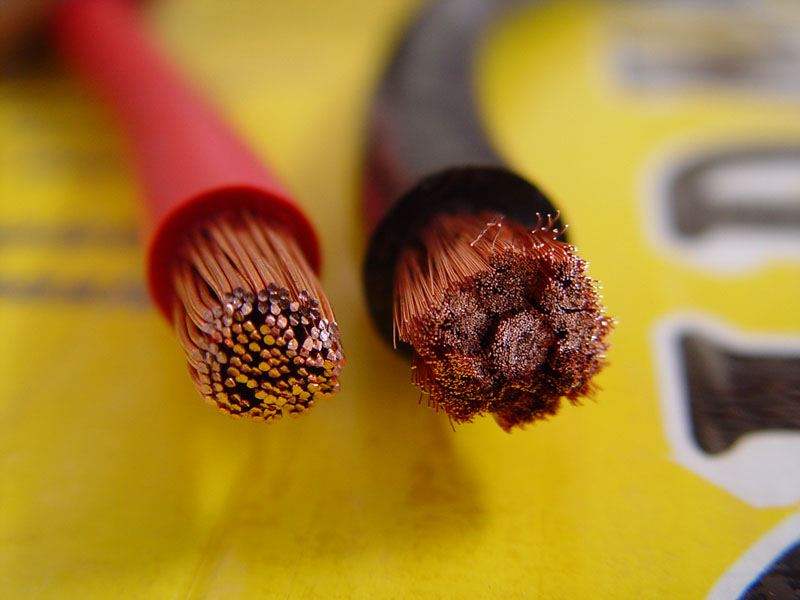
High strand cabling offers a range of advantages, including increased flexibility, reduced EMI, higher current-carrying capacity, enhanced durability in dynamic environments, improved electrical performance.
The “skin effect” is an electromagnetic principle that causes the current to concentrate on the surface of the conductor or wire, especially at high speeds. If there is not sufficient enough area to carry the current, it will find an alternative path and could cause operational issues (signal loss or distortion) or hardware damage.
Hundreds or thousands of strands make up high strand cabling which provides a much greater surface area than a solid conductor or standard strand cabling. Moreover, their vibration resistance and overall durability make high strand cables apt for challenging environments, providing longevity and resilience.
Effects of Low Strand Cabling in Variable Frequency Drives
Low strand cabling in Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) can lead to adverse effects on electrical performance and safety. The higher resistance of low strand cables can generate excess heat during power transmission, diminishing overall efficiency and risking overheating.
Voltage sag, a common concern associated with low strand cables, detrimentally impacts the performance of VFDs, inducing instability and the risk of motor overheating.
Poor shielding properties in these cables can lead to increased electromagnetic interference, impacting both the VFD system and nearby electronics. Moreover, the reduced flexibility and durability of low strand cables make them more susceptible to damage in industrial settings.
Safety concerns, including fire hazards, arise from heightened heat generation and potential voltage drop. Adhering to industry standards is critical, and selecting cables that align with VFD manufacturer recommendations is imperative for maintaining a reliable and secure VFD system operation.
Follow the Manufacturer’s Guidelines
Even if the highest quality cable is used it can be defeated if not installed properly. Shields and grounds should be connected at the drive and motor. Wiring for the machine’s PLC or IPC control components should be run separate from the motor power cable in order to prevent signal noise. Cable environment, bend radius, and other factors should be considered for where and how the cable is run.
Contact KEB for VFD Power Cables
Selecting a high quality motor cable and installing it properly will help prevent nuisance trips or hardware damage that can be caused by EMI. If you would like more information on VFD power cables, please contact an application engineer at KEB America.
Let's Work Together
Connect with us today to learn more about our industrial automation solutions—and how to commission them for your application.